In CPD Modules
CPD modules help to expand your clinical knowledge on a whole range of topics. Make sure you log your learning so you can track your progress and add to your online revalidation record.Bookmark
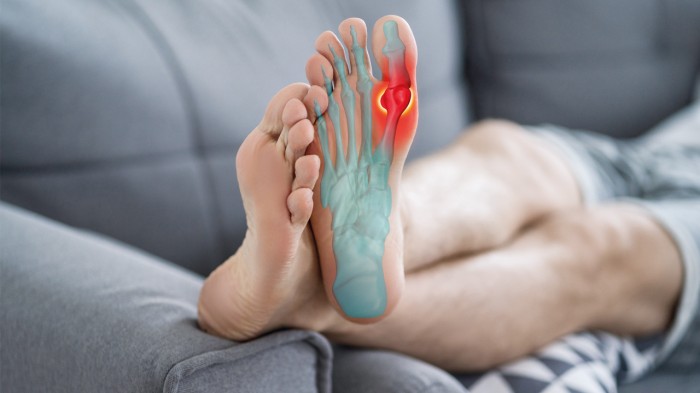
The module explains the symptoms of an acute attack and how it is managed, plus ways in which the risk of repeat episodes can be reduced and the incidence of complications lessened, which can be debilitating.
Key facts
- Gout is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis
- Acute attacks occur due to uric acid crystals accumulating in a joint, most commonly one of the big toes, causing severe pain, redness and swelling
- NSAIDs and colchicine are the two most common drug treatment options for acute episodes of gout
- Left unmanaged, gout can cause long-term problems including disability due to joint damage
- Allopurinol and febuxostat are the most frequently used urate lowering therapies (ULTs)
Contributing author: Asha Fowells MRPharmS MFRPSII, clinical pharmacy writer